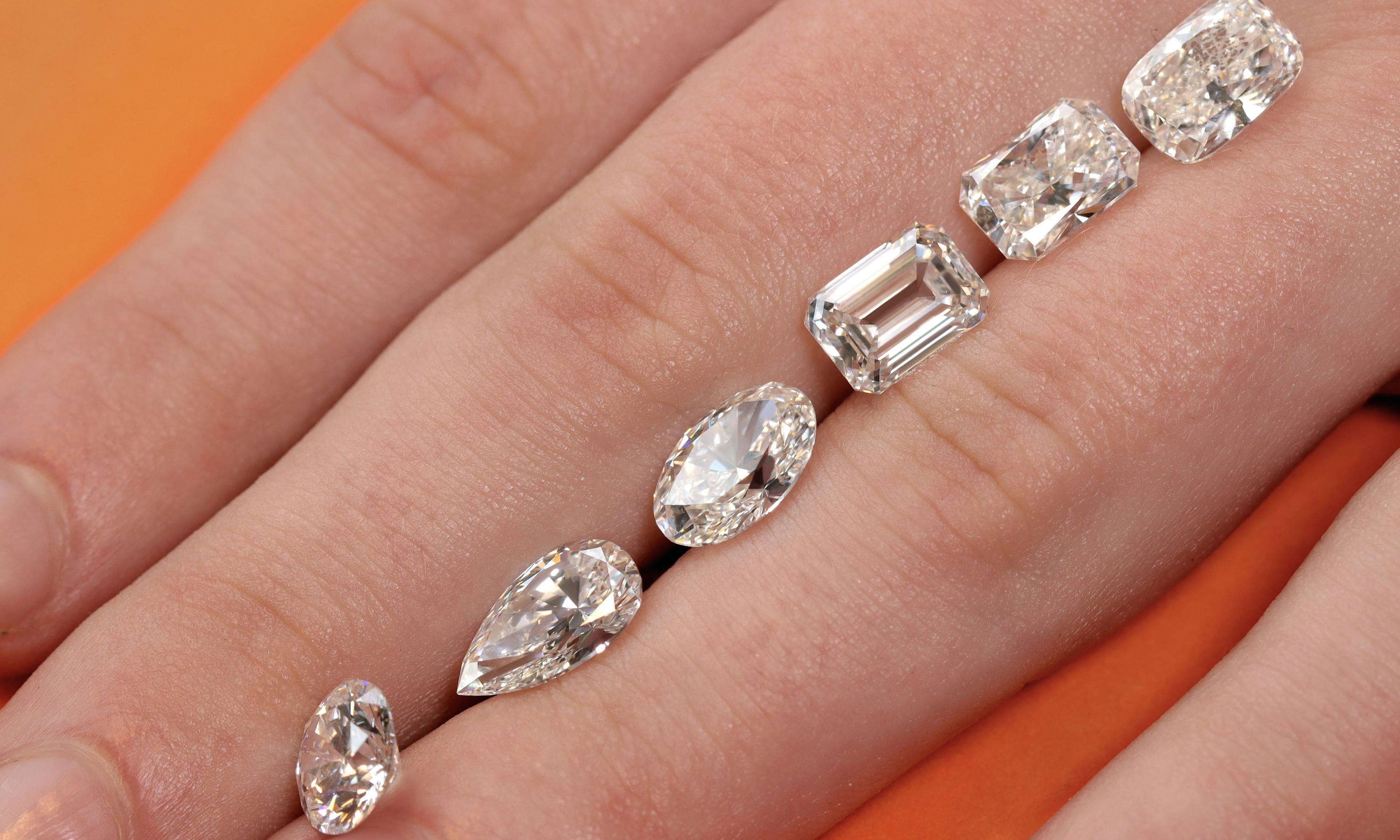
Diamonds, known for their rarity, beauty, and enduring symbolism, have long been coveted as one of nature’s most precious gemstones. However, with advancements in science and technology, the creation of artificial diamonds—also known as lab-grown or synthetic diamonds—has emerged as a groundbreaking development in the world of gemstones. These diamonds, which are chemically, physically, and optically identical to natural diamonds, are becoming increasingly popular for both their ethical appeal and environmental sustainability.
What Are Artificial Diamonds?
Diamantes artificiales are diamonds that are manufactured in laboratories rather than mined from the earth. Despite being created in controlled environments, these diamonds share the same carbon structure as natural diamonds and exhibit the same properties. The two main methods for creating artificial diamonds are:
- High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT): This method simulates the extreme pressure and temperature conditions that occur naturally in the Earth’s mantle. Carbon is subjected to high pressure and temperature to form a diamond crystal.
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): In this process, a carbon-containing gas (like methane) is heated to a point where carbon atoms separate and bond together to form diamond crystals. The process occurs in a vacuum chamber, allowing for precise control over the growth of the diamond.
The Key Advantages of Artificial Diamonds
- Ethical and Conflict-Free: One of the primary appeals of lab-grown diamonds is that they do not contribute to the environmental or humanitarian issues associated with traditional diamond mining. The diamond industry has long been linked to exploitative labor practices and environmental damage, often in conflict zones. Artificial diamonds offer a more ethical alternative for consumers who are concerned about these issues.
- Environmental Sustainability: Diamond mining is a resource-intensive process that has been criticized for its significant environmental impact, including habitat destruction, water pollution, and carbon emissions. Artificial diamonds, in contrast, have a much smaller environmental footprint. Creating diamonds in a lab consumes far less energy and does not cause the same degree of ecological harm as traditional mining.
- Cost-Effective: While natural diamonds are rare and expensive due to their geological origins and the complexities involved in their extraction, artificial diamonds are typically more affordable. This is because the processes involved in creating lab-grown diamonds are less resource-heavy and can be scaled up more efficiently, leading to lower production costs. As a result, consumers can purchase diamonds of similar quality at a fraction of the price.
- Customizable: Artificial diamonds can be produced in a wide range of sizes, shapes, and colors, offering a level of customization that is often not possible with natural diamonds. Furthermore, as the technology behind lab-grown diamonds advances, the ability to create diamonds with fewer imperfections is becoming more feasible.
The Science Behind Artificial Diamonds
Artificial diamonds are created from carbon atoms that are arranged in a crystal lattice structure, which is the same as that of natural diamonds. The primary difference between a natural diamond and an artificial one is the source of the carbon and the method of formation. In a natural diamond, carbon atoms have taken millions of years to crystallize under extreme heat and pressure beneath the Earth’s surface. Lab grown diamonds, however, form in a matter of weeks or months under controlled conditions in a laboratory.
The high-pressure, high-temperature method (HPHT) mimics the conditions deep within the Earth, where natural diamonds are formed. By exposing carbon to intense pressure and heat, a small diamond seed is used as a catalyst to encourage diamond growth. On the other hand, the CVD method uses a different technique, involving the deposition of carbon atoms onto a substrate, allowing the crystal to grow slowly and steadily in a controlled environment.
Both methods result in diamonds that are chemically indistinguishable from natural diamonds and exhibit the same brilliance, hardness, and durability.
The Growing Popularity of Artificial Diamonds
Lab-grown diamonds have gained significant popularity in recent years, particularly as more consumers become aware of the ethical and environmental benefits they offer. They are increasingly being used in engagement rings, fine jewelry, and even industrial applications, where their hardness and conductivity make them useful for cutting tools, electronics, and high-performance machinery.
The market for artificial diamonds is expected to continue growing as consumer demand shifts toward sustainable and ethical products. Major jewelry brands and retailers are beginning to offer lab-grown diamonds as an alternative to natural stones, further legitimizing their place in the industry. In fact, some reports suggest that the market for lab-grown diamonds could soon rival the traditional diamond industry in terms of both sales and consumer acceptance.
The Future of Artificial Diamonds
As technology continues to evolve, the future of artificial diamonds looks bright. Scientists are working to improve the efficiency and quality of the diamond-growing processes, potentially reducing costs even further. With the growing emphasis on sustainability, artificial diamonds may become the preferred choice for conscientious consumers who want to enjoy the beauty of diamonds without contributing to the negative impacts of mining.
Moreover, there is potential for artificial diamonds to be used in various new applications, such as in quantum computing, advanced electronics, and even in space exploration. The properties of diamonds—such as their exceptional hardness and thermal conductivity—make them ideal for a variety of technological uses beyond jewelry.
Conclusion
Artificial diamonds represent a significant leap forward in the world of gemstones. Offering the same beauty and durability as natural diamonds, they provide an ethical, sustainable, and cost-effective alternative for consumers. With their increasing popularity and the ongoing advancements in diamond production technology, lab-grown diamonds are likely to become a mainstay in both the jewelry market and beyond. As consumer awareness grows and technological innovations continue, artificial diamonds may very well redefine the diamond industry as we know it.